Optimising your Google Shopping campaign! It sounds a bit crazy and fancy. However, what does it actually mean?
It is clear that it corresponds to some actions and strategies. Tactics and tips that can help you get closer to your goals. These goals can be anything from a specific number of clicks to achieving a particular spend duration.
But the ultimate target is to boost your ROI. That’s what these Google Shopping optimisation tips are all about.
You should know that 85% of all product searches start from Amazon or Google. In fact, almost 76% of retail search ad spend is driven by Google Shopping ads.
So this is, no doubt, a huge platform that can help you build brand awareness and grow revenue. The first thing you’ll need to do is figure out where you’re at with your Google Shopping optimisation, and then follow our tips.
So let’s discuss some of the most effective ways that can optimise your Google Shopping campaigns.
Google Shopping optimisation tips
1. Research top brands
You can simply check the performance of brands by clicking on the ‘Brand’ button in the Dimensions tab.
My analysis starts with the Dimensions tab. It is easy to access and provides insight into several shopping campaign features. This tab will help you analyse the performance of different brands, just like it does for your individual products.
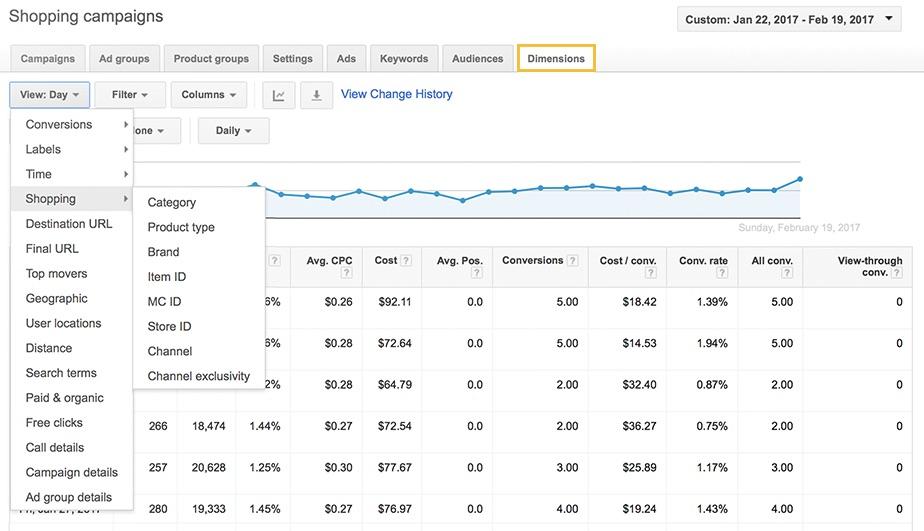
The foremost goal of analysing the brand and product performance is to divide and subdivide the product groups according to the specific brand. Let’s suppose you can easily analyse that bidding on Nike will be better for you if you are selling socks, since Nike has the highest profit margin. Your next step would be to exclude other things from the product group in order to produce a PLA containing a Nike product for sock-related searches.
2. Day-parting and geo-targeting
When it comes to Google Shopping optimisation tips, day-parting and geo-targeting are often forgotten. Some consider that they can’t be implemented in Google Shopping campaigns, but this is a misconception.
Implementing day-parting adjustments
You need to analyse when your conversion rates are highest or the lowest, by hour of the day or day of the week. For example, if you’ve noticed that your conversion rate is too high from 1am to 6am, you can simply apply bid modifiers. This will free up some budget so that you can bid more on traffic during your peak conversion times.
Continue to review your modifiers at least once a month, and make any changes you feel are necessary.
Using geo-targeting filters
In order to observe the performance of your campaign according to the country, region, city, metro area, or particular location, simply select the Geographic view.
The next step is to analyse how your campaigns behave area-wise. Look for the best and the worst regions for your campaign.
Now apply geo-targeting bid modifiers for each click from top-performing areas.
Make sure that you have enough data before you set your time and geo modifiers. Observe the behavior of your conversion for at least two to three months.
3. Identify search intent
For any paid advertising campaign is is important to understand every customer follows a purchase path.
This purchase path affects your bid. The higher the chances of purchase, the higher the bid will be.
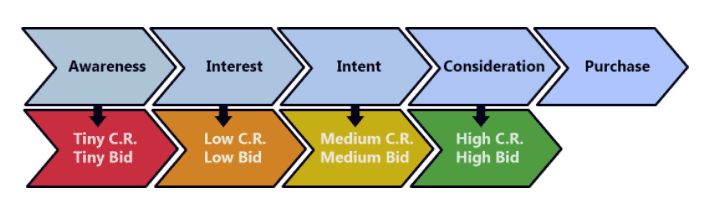
In order to identify the search intent of the visitor, you need to analyse their searched terms. These can be divided into five categories:
- Very low intent: includes generic product names like bikes or shoes
- Low intent: includes generic product categories, like mountain bikes or jogging shoes
- Medium intent: includes specific product categories, like 21 speed mountain bike or grass jogging shoes
- High intent: along with the category, this search term also includes specific product types, like 21 speed mountain bike with dual suspension, grass jogging shoes for men. It can also include brand names, for example Raleigh Mountain bikes or Nike jogging shoes
- Very high intent: includes the actual name of the brand, like Raleigh Helion 2.0 2017 or Nike Pegasus Trail 2 GORE-TEX
After analysing the search intent, you can simply apply the priority setting to your campaign.
4. Use negative keyword lists
Negative keyword lists can help you identify the user search intent. They also tell Google which search term should not trigger your campaign. It will stop Google from showing a product listing if a specific keyword is used by the user.
Advertisers use negative keywords to reduce wasted advertising costs. These are set for users who are not really looking to buy a product, or those who are looking for products you don’t sell. For instance, a search for ‘glasses’ could bring up drinking glasses and eyeglasses. If you only sell one of these, you don’t want to waste budget appearing for the other.
This can also work with new and used products. If you only sell brand-new items, you can add ‘used’, ‘second hand’ and ‘eBay’ to your negative keywords list.
5. Optimise your product feed
It is very important that your product feed is properly optimised. Google takes the data to display from the product feed.
It is very important that you make it easier for Google to read your product details so that it can display them in a better way.
There are a few attributes you should focus on:
Images
Google has some rules and regulations to follow when it comes to optimising images for your Shopping campaigns. Make sure you stick to them. You can also try A/B testing with images, colours and buttons.. For example, you can test if lifestyle or stock photos have a better effect on your click-through rate.
Product titles
Product titles hold the most important value when you are optimising your feed. Catch the interest of your customer by adding attractive words. Use the most appropriate word at the beginning that can engage your customer. A great way to optimise your product titles is by getting help from writing experts and tools like dissertation writing services, Grammarly and Hemingway App to create catchy taglines.
Prices
Make sure that the price and currency are always up to date for all of your products in your feed. This is where Google will pull its information from and you will be penalised if the information is incorrect. Also make sure to avoid common merchant errors as they have a high impact on the quality of your ads.
6. Structure your Shopping campaign
It is essential to structure your Shopping campaign properly. Since you don’t have a single bid for all products, each one has its own profit margin. Some will be more popular with a higher conversion rate, while others will be purchased less.
This is why Google allows you to categorise your products. You can use category, brand, conditions, item ID, product type and custom labels to divide your inventory.
You can do this in three simple steps.
Step 1: Start with any one product group, like All Products. Now click ‘edit’ and divide your products according to the attributes of your choice.
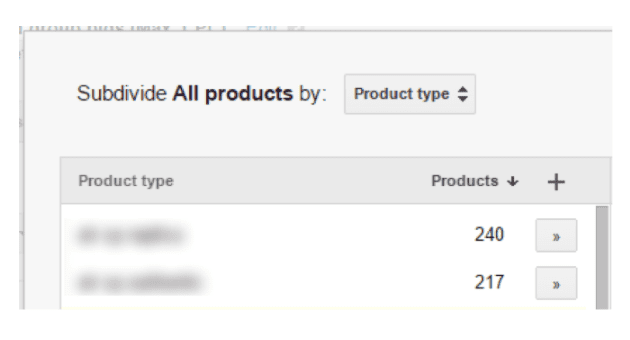
Step 2: The list of available values will now be in front of you. This data is pulled from your feed. You can easily create separate product groups using these values.
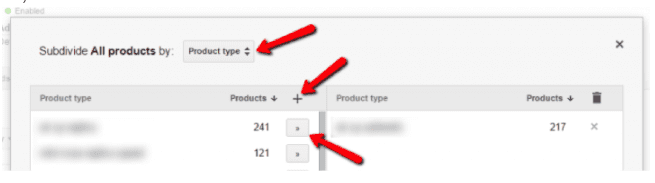
Step 3: Repeat the above process as many times as you want to create subdivisions.
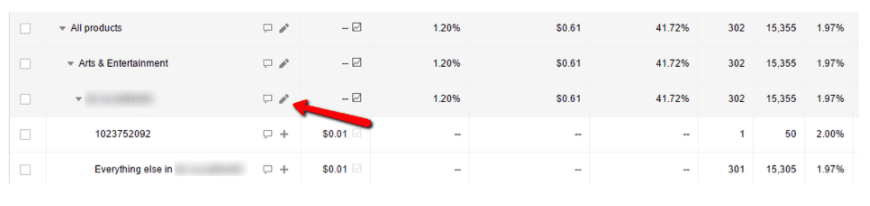
7. Adjust your bids
Once you have set the above structure for your Shopping campaign, Google Ads will show you another option under the product group named ‘Everything Else’. This allows you to set different bids for different products in each category, type, products and so on.
8. Effective reporting
Once you are aware of the dimension tab as discussed in the first tip, you will be able to analyse your Shopping campaign using:
- Item ID report: you will be able to see the KPIs for each product. Simply sort your products by clicks and explore the performance of each ID
- Search terms report: sorting it by costs and impressions allows you to have an in-depth analysis of the search terms
- Devices report: this allows you to find out which devices are used most by your customers so you can optimise your campaign
9. Avoid extreme changes
It’s important to note that you shouldn’t increase or decrease your bids by 20%. Google Shopping campaign optimisation works best with small alterations that are implemented for a reason.
You’ll also want to avoid making lots of changes at once. Make one or two small switches, then analyse the data for two or three months before deciding on your next move.
Up to you
Optimise your Google Shopping campaigns using these tips and you’ll be well on the way to achieving your targets. Make sure you’re consistent with your plans, and the rest will work for you for sure.
About the author
Amanda Jerelyn is currently working as Marketing Manager at Dissertation Assistance. She is a tech geek and keeps herself busy traveling and reading blogs. Amanda also blogs at Guide2Write. She loves to help students with their academics and provides them online assistance.







