Some people lose sleep over ghosts, ghouls and poltergeists. Others are scared of vampires and werewolves. Then there are digital marketers.
What makes digital marketers lose sleep at night? We’ve asked some staff at Team Tillison what they’re scared of finding in their closet or the backend of a website, and we’ve compiled the ultimate guide on how to defeat them.
The scariest digital marketing problems in 2022

Slow page speeds and failing core web vitals
We all know how important page speed is for user experience and SEO. If your website loads slowly, you’ll lose leads, conversions and rankings – a digital marketing problem no one wants to have. It can also affect your position in search engine results (SERPs).
So how can you combat this ghoulish issue?
First, be aware of what’s important and what everything means. First contentful paint replaced first meaningful paint in 2020 as being an important factor in your page speed. This means that Google is now paying more attention to how long it takes your largest content element to load.
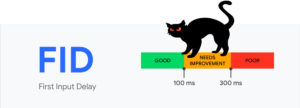
The three main core web vitals you need to be aware of are Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID) and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). Each of these measures a different aspect of a page in terms of user-friendliness.
- LCP measures loading time, in other words, how long it takes the largest element on your page to load.

- FID measures how long it takes your page to become interactive, which is when a user can start interacting with your page.
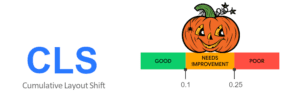
- CLS is a measurement of visual stability, in other words, how much the elements on your page move around as the page loads. The less stable your page is visually, the more the elements move around.
Measuring your core web vitals is another challenge. You can use Google’s tools like PageSpeedInsights and the handy reporting section in Google Search Console to determine if there are any issues with your core web vitals. From here, you can see which areas you’re having trouble with and places where there are opportunities you can improve.
It’s important to bear in mind that when you’re looking at the data given to you from some tools, not all of the core web vitals are replicable in the lab environment they test in. This means that you need to be aware that FID is replaced by Total Blocking Time, which is a similar measurement to FID.
Keep paying attention to your page speed and taking note of your core web vitals using Google’s tools. Check what opportunities there are to improve page speed, like minifying your JavaScript and CSS like you were doing before. Even a tiny improvement in page speed can have a big impact.
Devilish duplicate content
Duplicate content can cause major problems for your site, as it can mean that search engines don’t know which URLs to rank for certain queries. This is because content that is too similar on multiple pages can also give users a negative experience, which is something search engines try to avoid giving to users.

How do you deal with duplicate content?
Ensuring that all your pages are unique, and providing users with high-quality information that answers their queries to the right depth is the easiest way to avoid duplicate content. If you have several pieces of content that are similar, or not detailed enough, you should consider whether consolidating them would help make them a better piece of content that gives a more thorough answer to a user’s query. If you use WordPress, it can be relatively easy to spot and fix duplicate content – especially if you’re utilising content templates. Though, if you need help with this, it’s never a bad idea to consult a WordPress SEO agency to get their help!
Accidentally deleting a Google Ads campaign
Sometimes you need to pause a Google Ads campaign. Perhaps you’re temporarily focusing on another part of your business, or you’re low on inventory so you need to hit that pause button. Whatever the reason, imagine the horror when you accidentally remove the campaign instead.
It’s something that keeps many PPC specialists up at night. But it doesn’t have to, because all is not lost.
While you can’t reactivate deleted campaigns, it’s honestly not the end of the world. You can still find your old campaign in the Ads Editor dashboard. Once you’ve got it, you can copy most of the information over to a new campaign.
The main problem you’ll have is that the data you’ve collected is now gone. You’ll need to build it again from scratch. However, this digital marketing problem isn’t the end of the world. You haven’t lost absolutely everything, and you can rebuild.
Lost in translation: using hreflang attributes
If there’s one thing that’ll make a Search Engine Optimist panic, it’s languages. If your website is global and has content and landing pages in a range of languages, each one needs its own hreflang. This means that search engines know which pages to show to users in each country.
Hreflang doesn’t have to be as confusing as many make it out to be – it’s a digital marketing problem that is sometimes blown out of proportion.
If you’re an international Search Engine Optimist, the hreflang attribute will soon become your best friend. It can go in one of three places on your website:
– On-page Markup
– HTTP header
– Sitemap
So let’s imagine you’re selling wine in France, Spain and Portugal. Your hreflang attributes will look something like this:
<link rel=”alternate” href=”http://domain.com” hreflang=”es-es” /><link rel=”alternate” href=”http://domain.com/fr/” hreflang=”fr-fr” /><link rel=”alternate” href=”http://domain.com/pt/” hreflang=”pt-pt” />
You’ll notice that your hreflangs look like they’re repeated – you have es-es, fr-fr and pt-pt. This is because it’s denoting language and country. ‘es-es’ is Spanish and Spain; if you were targeting Mexico, you’d have ‘es-mx’. To find the codes you need, just use ISO 639-1 for languages and ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 for territories.
One thing you will need to remember is that while hreflang works for Google and Yandex, Bing uses a different format. For this, you’ll need to use language meta tags instead.
Forgetting the sitemap
Almost every website needs a sitemap. It’s how search engines get from page to page when crawling your domain, and it’s essential if your site:
- Is really large
- Has a lot of content pages that aren’t linked to each other
- Is new and doesn’t have many external links
- Has a lot of videos and images
- Is shown on Google News
Building a sitemap can seem like an insurmountable task. How do you make sure you have everything in there that you need? How do you submit it?
The answers are simpler than you might think. All you have to do is follow these simple steps:
- Decide which pages on your website you want search engine bots to crawl
- Figure out which version of each page you want to be the canonical one; this means you can avoid using up your crawl budget on both the desktop and mobile versions of the same page
- Choose your sitemap format – most people go with XML
- Create your sitemap manually, or use a third-party tool to do it for you
- Add your sitemap to your robots.txt file or submit it to Google Search Console
That’s it. There’s nothing to be afraid of. Google even has a handy page with the guidelines you should follow when building your sitemap.
Click Fraud Goblins and Ghouls
There’s nothing worse than spending your time and money setting up a Google Ads campaign to drive traffic to your website, only for you to ultimately become a victim of click fraud ghouls and goblins.
For those lucky enough to not be affected by click fraud, it is essentially where a person or a bot repeatedly clicks on a Google Ad to waste its budget or in the worse case charge the owner more than they should be paying.

So how can you avoid the curse of click fraud?
Well, Google has put practices in place that try to combat click fraud through algorithms, which analyze clicks and impressions so that they can attempt to detect false traffic.
With this said there are still ways you can try to push back against click fraud, by using click fraud prevention platforms like ClickCease, AppsFlyer, Singular, PPC Shield and many more.
Hannibal the Page Cannibal
Ever spent hours researching keywords to optimise or build a new webpage, only to index it and come back a few days later to see it’s been gobbled up by a page with a similar keyphrase? Well, you my friend have met Hannibal the page cannibal, and he’s just chomped down on your webpage with some fava beans and a nice Chianti.
Cannibalization of a page occurs when you have one or more pages that are targeting the same or similar keyphrases.
So how do you fend off Hannibal the Page Cannibal?

Essentially your aim is to strengthen the ranking signals for the page, let’s say you had a page for a wedding venue SEO agency and one for a wedding venue Google Ads agency and one page was cannibalizing the other because of the keyword similarity. You want to show Google that the context of these pages are both different, internal and external links are a great way to show Google that although these pages seem similar they are completely different, you just need to make sure that the anchor text you are linking to is very specific to the context of the page

We hope this has put some of your fears at bay. In case it hasn’t, leave us a comment about your scary digital marketing problems or tweet us @TeamTillison and we’ll get our ghostbusters on the case.







